Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals the function of SoCER4 in alkanol synthesis in sugarcane
Yuting Zhou, Sangui Yi, Shuangcai Li, Zongling Liu
Funct Integr Genomics; 2025 Aug 2; 25(1):165. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01672-4.
Abstract
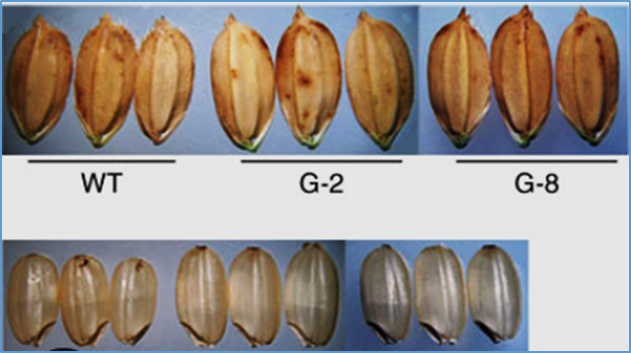
The wax of sugarcane buds, especially alkanol, was correlated to sugarcane smut resistance in previous studies. Moreover, alkanol could induce smut teliospore germination. This study aimed to analyze wax-related genes in sugarcane buds. In this study, the wax contents in germinated sugarcane buds from smut-resistant Zhongzhe 9 (ZZ9) and smut-susceptible Guitang 42 (GT42) were measured, showing that total wax content and alkanol content of GT42 were significantly higher than that of ZZ9 after bud germination. The gene expression profiles of germinated buds from ZZ9 and GT42 were analyzed using transcriptome analysis, and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) terms for cutin, suberine, and wax biosynthesis were enriched between ZZ9 and GT42. In addition, a lipid transfer protein (LTP) gene (c97015.graph_c0) may be involved in wax transportation that caused higher wax content in GT42 buds, and a SoCER4 gene (c120140.graph_c0) may play a key role in alkanol synthesis that caused higher alkanol content in GT42 buds. Here, the SoCER4 gene was functionally characterized via overexpression in Nicotiana benthamiana. The alkanol contents of SoCER4 transgenic N. benthamiana leaves were significantly higher than that of wild type, indicating SoCER4 was responsible for alkanol synthesis. These results would be helpful in understanding alkanol synthesis in sugarcane buds.
Số lần xem: 15
-
{mota}
-
{mota}
-
{mota}
-
{mota}
-
Biochar in the circular bionutrient economy
{mota} -
{mota}
-
Progress in Transcriptomics and Metabolomics in Plant Responses to Abiotic Stresses
{mota} -
{mota}
-
{mota}
-
Fine mapping and prediction of a candidate gene for wrinkled rind in melon (Cucumis melo L.)
{mota}